Outlook certificate errors can be a daunting issue, impacting not only Outlook in Office 365 but the entire browsing experience.
While common reasons include insecure email server connections and invalid SSL/TLS certificates, our experience revealed broader browser challenges. This guide not only acknowledges these common causes, but also shares practical solutions.
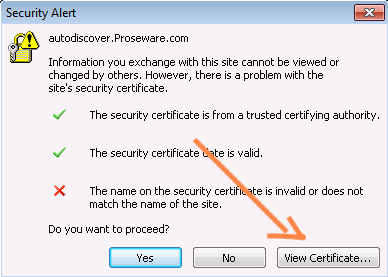
Before diving into fixes, you should verify the certificate name first.
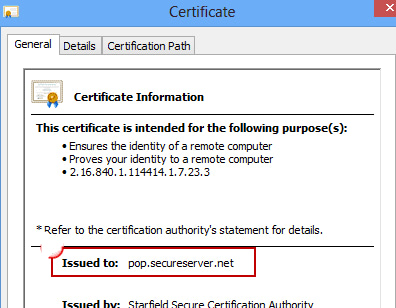
To do so, go to the pop-up error message and click on the view certificate. Navigate to the “Issued to Name” option and confirm whether the name indicated on the certificate matches that of the mail server.
If there is a disparity, correct the information and then restart Outlook.
Now, let’s move on.
Here’s how we fixed the Outlook certificate error:
1. Change Autodiscover DNS Records (Internal, External, or Both)
This method should not be taken lightly because if you misconfigure the DNS records, the Autodiscover feature won’t work properly.
So, why is this feature so important?
Actually, it’s a bit complicated. Let us explain this scenario in the easiest manner possible.
Autodiscover is a feature in Microsoft Exchange that automatically configures user profile settings for clients like Microsoft Outlook. It simplifies the setup process by automatically discovering and configuring the necessary server settings, eliminating the need for users to manually input details like server names, ports, and encryption methods.
In terms of DNS records, Autodiscover relies on specific DNS entries to locate the Autodiscover service.
These DNS records typically include the Service (SRV) record and the Autodiscover domain (CNAME) record.
The SRV record helps the client find the Autodiscover service endpoint, while the CNAME record points to the domain where Autodiscover settings can be retrieved.
Follow the steps below to change the autodiscover DNS records:
- Open the command prompt or Windows PowerShell.
- Run the nslookup command:
nslookup -type=srv _autodiscover._tcp.yourdomain.com
Here, replace yourdomain with the name of the domain from the issued certificate.
- Check A or CNAME Records (Optional) using the following command:
nslookup autodiscover.yourdomain.com - Update DNS records by running the NSLOOKUP with Set Type by the following command:
nslookup - Set the query type, set type=srv
- Add or modify the SRV record:
_autodiscover._tcp.yourdomain.com - Enter the new values as prompted
- Type exit to close the NSLOOKUP session.
Note: Remember to replace yourdomain.com with your actual domain, and ensure you have the necessary permissions to update DNS records.
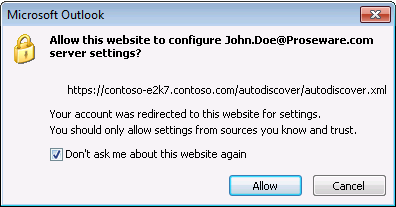
When an Outlook client utilizes the SRV record, it may prompt the user with a notification about the upcoming redirection. It is advised for the user to select the option “Don’t ask me about this website again” to prevent the recurrence of this message.
2. Disable Third-party Apps
If your Outlook is showing problems after you installed a third-party add-in then this solution is for you.
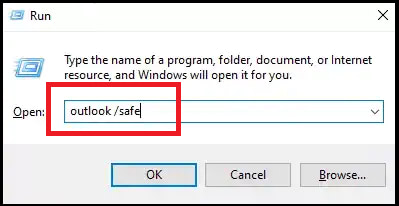
Press the Windows+R key to open the RUN dialog box. Now type outlook/safe to open Outlook in safe mode.
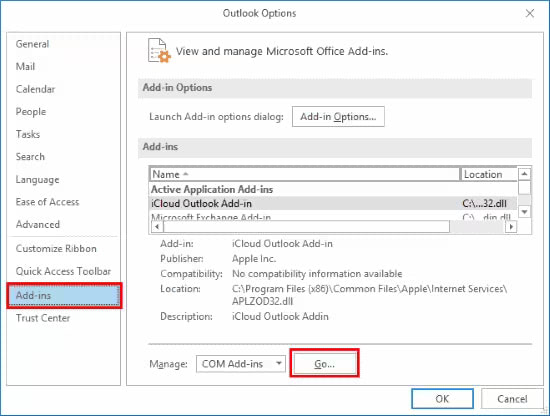
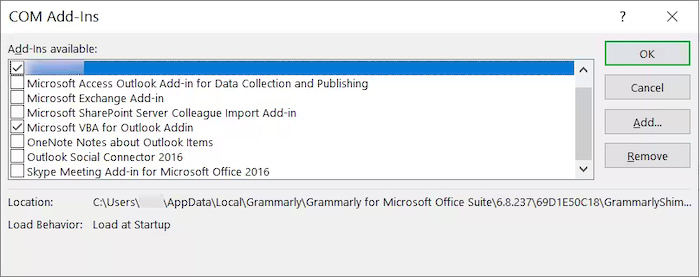
Now go to File> Options>Add-ins. Select COM Add-ins from the Manage dropdown menu at the bottom of the tab and click on GO.
Uncheck any faulty or unwanted add-ins and restart outlook.
3. Use Non-SSL Ports
Certain networks, especially in educational institutions, may block SSL ports for email servers, leading to an Outlook security certificate error in Office 365.
To address this, users can consider using non-SSL ports, such as POP 110, IMAP 143, and SMTP 587, which might not be blocked on the network.
It’s emphasized that while these non-SSL ports offer a workaround, they come with a potential risk of data theft.
4. Use Hosting Domain Name as Mail Server
Use the domain name of the hosting company as the mail server instead of your own domain name when using shared hosting.
This is suggested due to potential security issues arising from shared hosting providers not consistently renewing SSL certificates for each individual domain hosted on the shared servers.
How to Enable SSL in Outlook
Enabling SSL in Outlook is crucial for ensuring the security and privacy of your email communications.
SSL is a protocol that encrypts the data exchanged between your email client (Outlook) and the email server, making it significantly more challenging for unauthorized parties to intercept and decipher the information.
By using SSL, you create a secure, encrypted connection for both incoming and outgoing email servers.
Here are the steps to enable ssl in outlook:
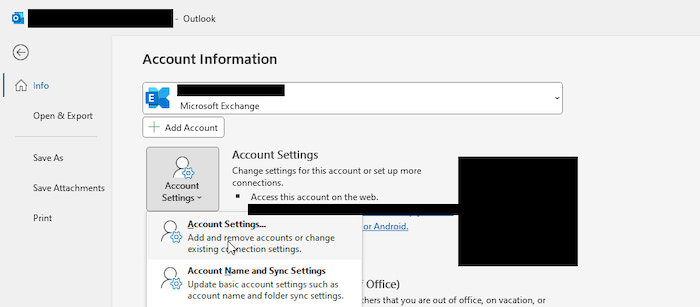
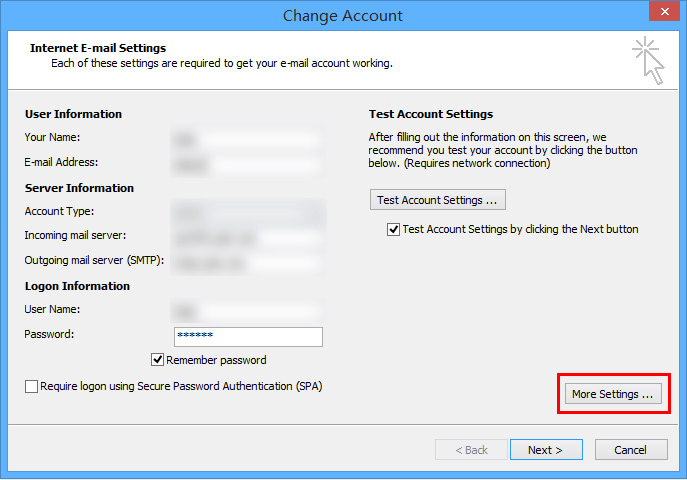
- Open Outlook and navigate to File > Account Settings > Account Settings.
- Choose your email account and click Change.
- Adjust the Incoming mail server and Outgoing mail server (SMTP) settings to mail.example.com, replacing “example.com” with your actual domain name.
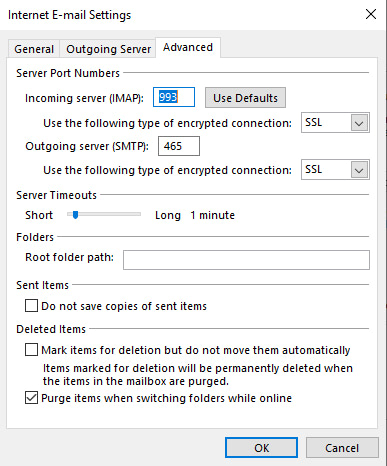
- Click on More Settings.
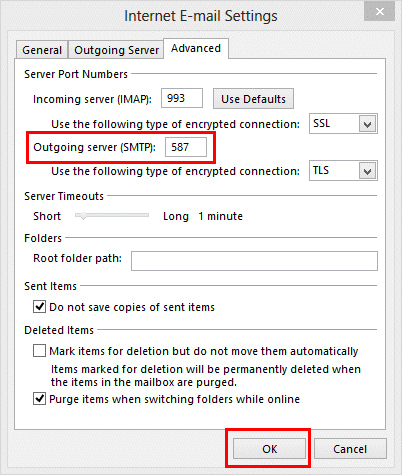
- In the Advanced tab, for IMAP accounts, set Incoming Server (IMAP) to use SSL and Outgoing Server (SMTP) to use SSL. For POP3 accounts, check the box for “This server requires an encrypted connection (SSL)” under Incoming Server (POP3) and set Outgoing Server (SMTP) to use SSL.
- Click OK.
- Click Next and then Finish to complete the email account configuration.
Types of Outlook Certificate Error Messages
According to our compiled data, there are 3 types of certificate error messages.
- Type 1
- Type 2
- Type 3 Error
Type 1 Error Message
Error Code: 0
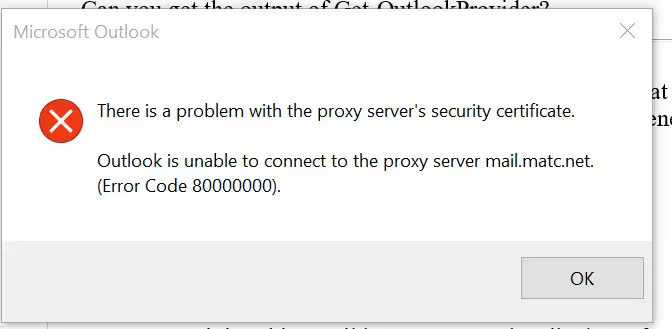
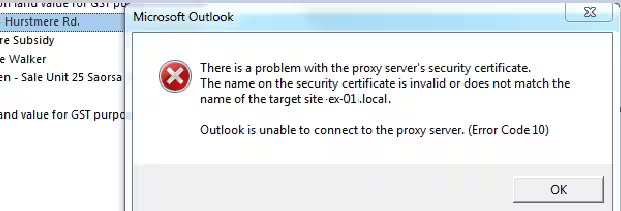
Type 2 Error Message
Issue: A problem persists with the proxy server’s security certificate, causing Outlook to be unable to connect to the specified proxy server (e.g., mail.matc.net).
Error Code: 00000000
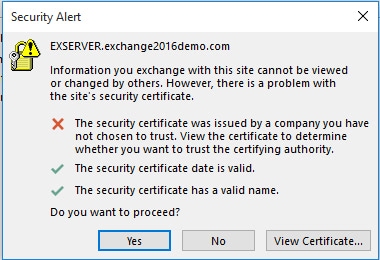
Type 3 Error Message
Issue: The security certificate is from an untrusted certifying authority, indicating that the certificate was issued by a company that the user has not chosen to trust. The user is prompted to view the certificate and decide whether to trust the certifying authority.
Error Code: 00000000
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What is an Outlook certificate?
Answer: An Outlook certificate, often referred to as an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate or a digital certificate, is a security feature that enables secure communication between Outlook and the email server. It encrypts the data exchanged between the email client (Outlook) and the mail server. The main reason for installing an Outlook certificate is that sensitive information, such as login credentials and email content, remains private and secure.
Question: What causes Outlook certificate errors?
Answer: Certificate errors in Outlook typically occur when there’s an issue with the SSL certificate configuration. Some reasons include: Expired SSL certificates, incorrect certificate configuration, self-signed certificates, missing certificate chain, and revoked certificates. When Outlook encounters a certificate error, it typically warns the user and provides options to proceed or reject the connection.
Final Words
This comprehensive guide equips users with insights and solutions to tackle Outlook certificate errors comprehensively.
Resolving Outlook certificate errors demands a nuanced approach, considering various factors such as Autodiscover DNS records, add-ins, network configurations, and SSL usage.